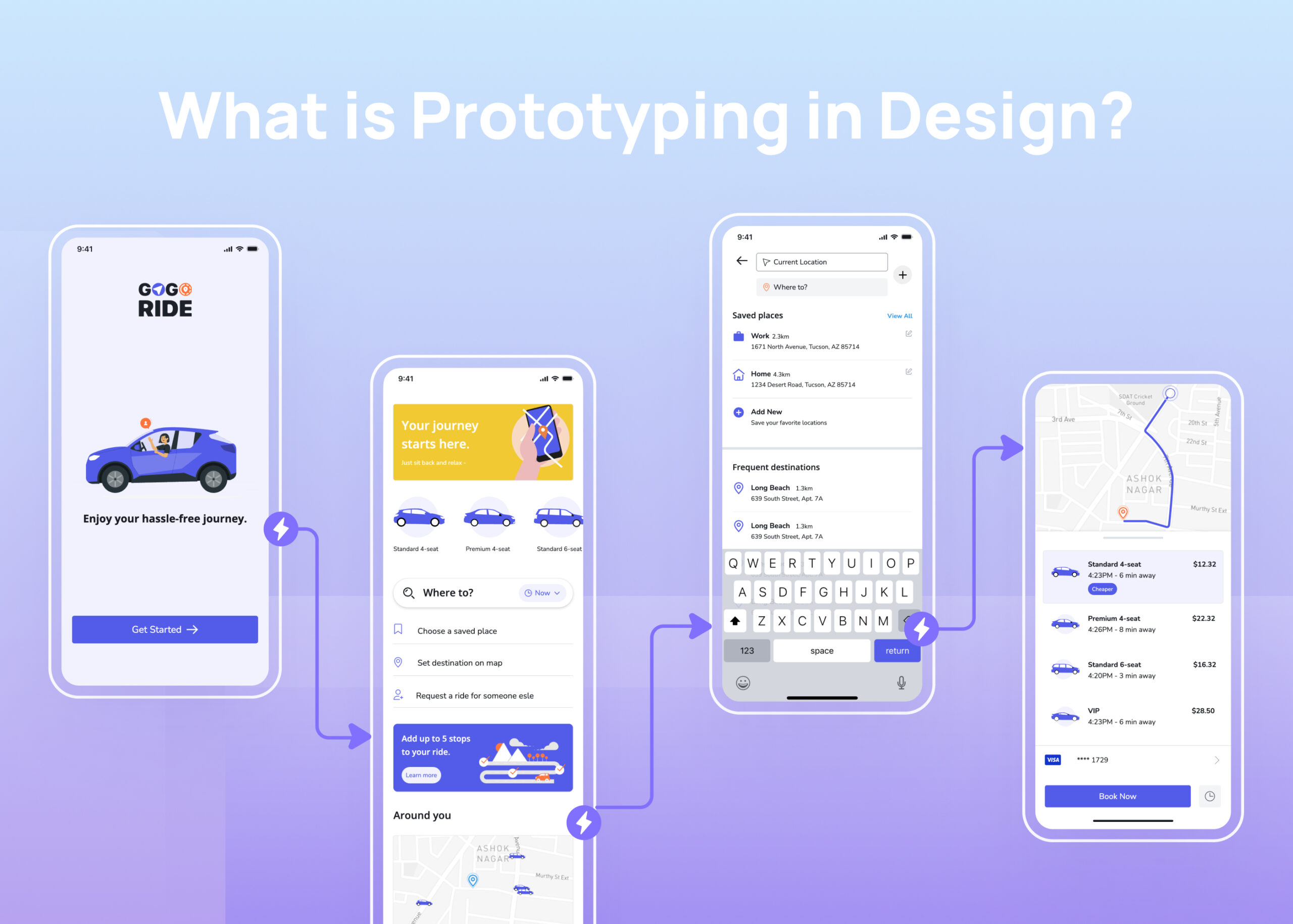
Developing a new digital product like a website or app involves many steps in the design process before reaching the final version. Prototyping plays a key role by allowing designers and product managers to test ideas and get feedback from the stakeholders early on. Before investing time and money into coding a digital interface, prototypes represent user flows and interfaces. Methods range from paper prototypes using basic materials to high-fidelity digital prototypes that feel interactive.
Prototyping helps identify usability issues, validate ideas, and determine unnecessary features. This blog post explains what prototyping is in digital product design, and their different fidelity levels. We’ll outline the prototyping process with Visily. Let’s get started!
What is Prototyping in Design?
Prototyping in design is the process of creating and testing mock-ups of a digital product like a website or app before it is fully developed and launched. Before the stakeholders invest time and money into coding the final product, they create prototypes to represent user interfaces and test ideas.
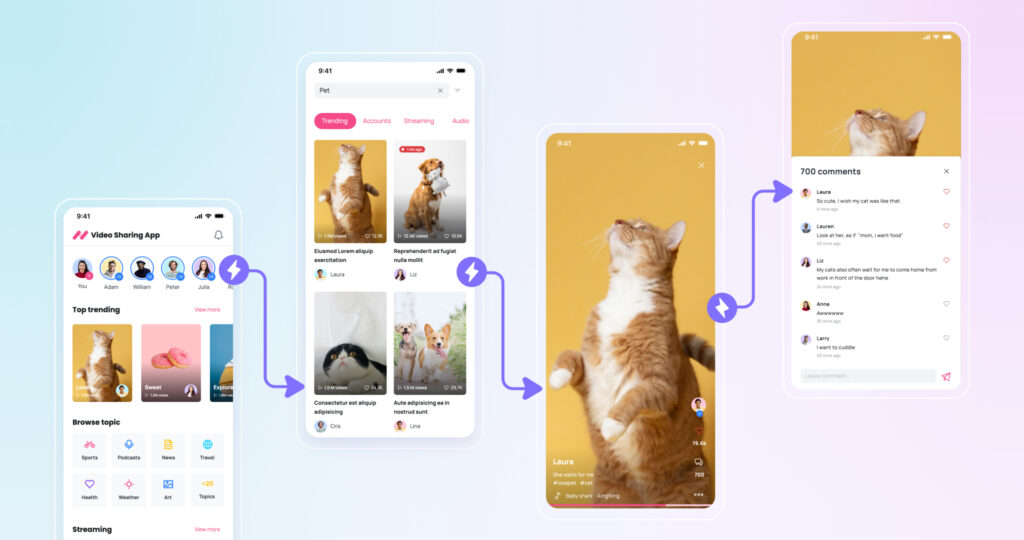
There are many methods of prototyping. Low-fidelity prototypes are simple versions made of paper or basic digital layouts. They help teams test basic ideas and workflows early on without much detail. As the design progresses, higher fidelity prototypes add more visual details and interactivity to feel closer to the final user experience. Digital tools like Visily allow to connect screens and test flows.
Popular formats include paper prototypes with hand-drawn elements as well as digital prototypes created in programs like Visily and Figma. Paper allows quick mockups while digital versions easily show working flows and add multimedia content. The goal is focused on user feedback rather than mass production.
The iterative prototyping process helps perfect prototypes over multiple sessions. Testing identifies usability problems and unnecessary features early, saving significant rework later. Refined prototypes ensure teams design interfaces and experiences matching user needs before moving to development. This validation reduces risks and creates better products.
Why is prototyping important?
Prototyping is important in digital product development. It allows designers, developers, and product managers to test and improve their ideas before developing the final product. Some of the benefits of prototyping are:
Tests Concepts
Prototyping allows design teams to gather feedback from the stakeholders early in the process before committing to full development. Simple and inexpensive interactive prototypes represent initial ideas to test with the stakeholders. Observing interactions uncovers pain points and flaws not visible in assumption-based designs. This real user testing from the stakeholders helps perfect prototypes and ensure final products match genuine user needs.
Speed Up the Process
Prototyping can be done faster than coding. It also helps to get feedback from the stakeholders in the early stages. Thus an interactive and digital prototype speeds up the development process of a digital product.
Communication
Prototyping helps to communicate the design vision and functionality to the stakeholders. Without relying on lengthy documentation or explanations prototyping facilitates collaboration among the designers and other stakeholders.
Accuracy
Prototyping helps to ensure that the design meets the user’s needs and expectations. It also determines the technical requirements and specifications of the product. Prototyping also allows for testing of the design for usability, accessibility, and performance.
Accelerates Final Design
The iterative process of refining multiple prototypes helps teams align, gain confidence, and accelerate decisions. Rapid changes and convenient copying in digital tools like Visily and Figma permit the exploration of more concepts. Constant feedback from multiple stakeholders resolves questions so talented coders invest more time constructing quality interfaces instead of redos.
Types of Prototypes
Different prototyping styles have benefits depending on what the team needs to learn.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid or throwaway prototyping refers to the creation and use of prototypes with limited functional capability, but sufficient to provide a way of rapidly evaluating different approaches. Rapid prototypes provide quick and inexpensive testing in the early stages of the design process. In this prototyping method teams sketch concepts on paper prototypes or simple digital layouts to visualize ideas.
Such prototypes are used in user testing sessions to get early feedback, validate assumptions, and uncover potential usability issues. Since they are fast and easy to change, teams can iterate rapidly based on user input to fail early if needed before investing significant time and money.
Evolutionary Prototyping
Evolutionary prototyping in the digital product development process refers to the generation of a series of prototypes that incrementally build upon each other across the course of development.
An evolutionary prototype starts simply but turns into a functional prototype through multiple digital iterations based on continuous feedback from the team and stakeholders. An initial paper prototype might represent key screens and flows. User input then helps transform this into digital prototypes with increasing interactivity and features. This collaboration enables the prototype to evolve towards meeting user needs but can risk straying too far from early strategic goals.
Incremental Prototyping
Incremental prototyping is a development methodology in which individual prototypes are built separately in parallel, evaluated, and then merged into a comprehensive whole. This approach is often used in enterprise software development where many modules and components are related loosely.
In incremental prototyping, design teams work together to create consistency in look, feel, behavior, and terminology by defining guiding principles in advance. Each prototype is built with a focus on producing a specific feature. Then it is tested and improved upon, allowing for rapid iteration of the product. This method can help to accelerate the process of creating a working model, by testing each feature individually and continuously improving.
Extreme Prototyping
Extreme prototyping is an agile software development practice that involves building a working prototype of a web application before any back-end services implementation. This process intends to get feedback from the stakeholders to decide the best approach for development and to avoid costly redesigns. In extreme prototyping, three phases are followed. First, wireframes are built to simulate the presentation layer. Then created HTML pages are tied with the simulated services layer. Lastly, the services layer is coded and implemented.
This approach allows the user interface to be developed first and is a great way to ensure the design is right for the user before investing too much time and resources in backend development. Extreme prototyping helps reduce design risks, detects errors early, makes iterative development possible, and reduces overall development time and costs.
The Prototyping process
1. Define Goals and Requirements: Start by clearly defining the purpose and goals of your prototype. What do you want to learn or test? What features or functionality should be included? Identify the key user flows and interactions to focus on.
2. Choose the Right Fidelity Level: Determine the appropriate fidelity level for your prototype based on your goals and the stage of the design process. Low-fidelity prototypes are quick and cheap, ideal for early-stage testing. Mid-fidelity prototypes add more detail and interactivity. High-fidelity prototypes closely resemble the final product.
3. Select a Prototyping Tool: Choose a prototyping tool that suits your needs and skill level. Tools like Visily offer a range of features for creating interactive prototypes quickly and easily. Consider factors like collaboration, ease of use, and integration with other design tools.
4. Create the Prototype: Begin building your prototype using the selected tool. Start with the main screens and user flows, adding interactivity and transitions as needed. Use placeholders for content and focus on the overall structure and navigation.
5. Test and Iterate: Once your prototype is ready, conduct user testing sessions to gather feedback. Observe how users interact with the prototype and identify any usability issues or areas for improvement. Based on the feedback, iterate and refine your prototype until it meets the desired goals.
Qualities of a good Prototype
A good prototype should have the following qualities:
Clarity: The prototype should clearly communicate the design concept and user flow. It should be easy to understand and navigate, even for users who are not familiar with the product.
Interactivity: The prototype should allow users to interact with the interface and experience the key functionality. This helps in gathering valuable feedback and identifying usability issues.
Relevance: The prototype should focus on the most important features and user flows. It should be tailored to the specific goals and objectives of the project.
Efficiency: The prototype should be created quickly and efficiently, without spending too much time on unnecessary details. It should be easy to modify and iterate based on feedback.
Fidelity: The prototype should have the appropriate level of fidelity based on the stage of the design process and the goals of the project. Low-fidelity prototypes are suitable for early-stage testing, while high-fidelity prototypes are better for final validation.
Low Fidelity vs. Mid Fidelity vs. High Fidelity Prototypes
Prototypes represent ideas at different levels of fidelity – how closely they resemble the final product visually and functionally. The level of fidelity impacts the feedback teams can gather.
Low Fidelity Prototypes
Low-fidelity (lo-fi) prototypes provide the simplest representations of concepts. A low-fidelity prototype with rough sketches and handwriting allows teams to quickly mock up flows and layouts before coding begins. While visuals remain basic at this initial prototype stage, understanding how users interact and listening to feedback from the teams and stakeholders uncovers vital insights on improving workflows, interfaces, and features with minimal investment of time and money.
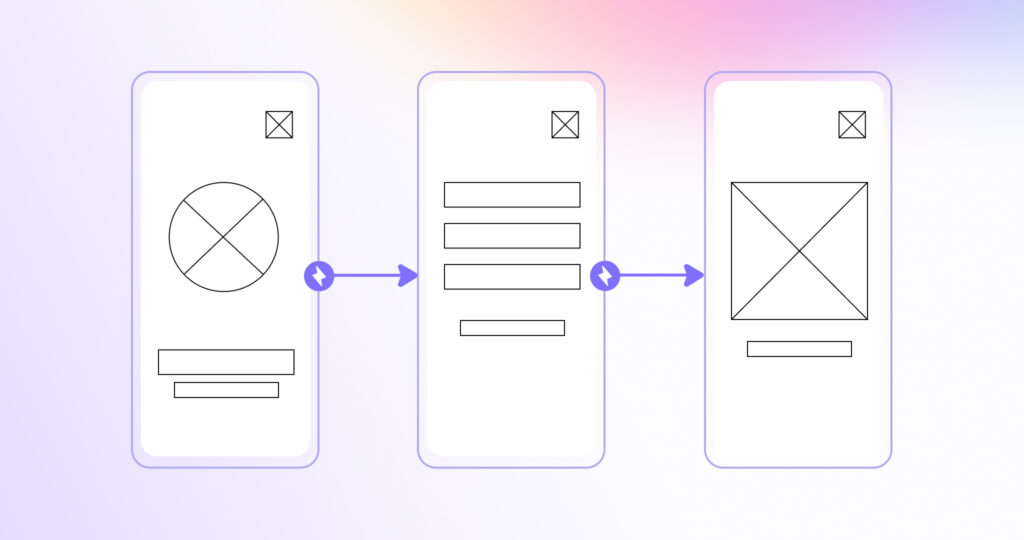
Their simplicity and low cost facilitate experimentation, rapid changes, and ultimately creating better user experiences in the final product. Teams gain confidence in ideas before sinking resources into high-fidelity representations closer to the final.
Mid Fidelity Prototypes
Mid-fidelity prototypes are interactive prototypes that have more detailed design elements than low-fidelity prototypes. But still, high-fidelity prototypes are more detailed. These types of prototypes typically present interactions that are relatively close to how the final product will behave. The visual design may be quite rough, but any animation, navigation, and user flow will have been designed to represent the intended behavior.
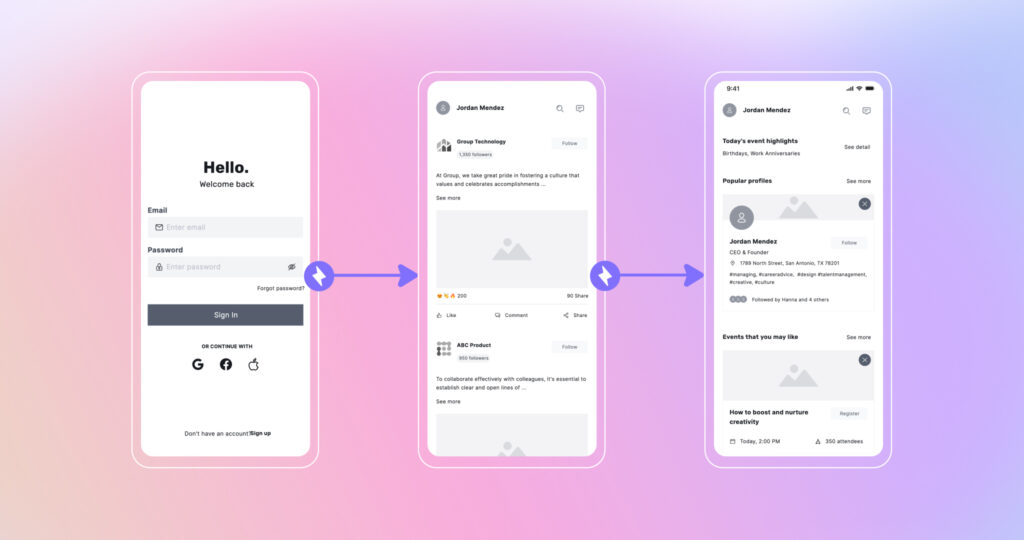
Still cheaper and faster to change than hi-fi, mid-fi prototypes enable testing of information architecture, navigation, interface layouts, and interactive elements to shape designs and flows. Users experience basic working UI (User Interface) components, copy, graphics, and operating logic while visuals, content, and styling remain in draft quality.
High Fidelity Prototypes
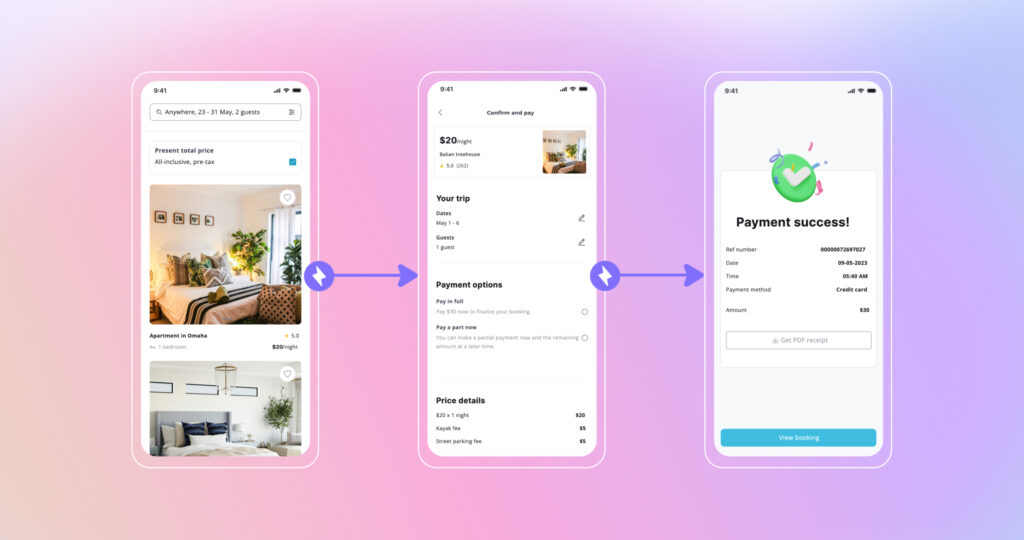
A high-fidelity prototype closely mirrors the final product in appearance, functionality, and interaction at a scaled-down scope. Digital tools create detailed and realistic views using actual branding, polished visuals, imagery, motion, and effects you would expect in a finished design. Links between screens demonstrate step-by-step user flows and complex logic.
To learn more about the differences between prototypes and other design artifacts, check out these articles:
- Mockup vs Prototype: What’s the Difference?
- Wireframe vs Prototype: Understanding the Key Differences
- Prototyping in Agile Development: Best Practices and Tools
How to create a Prototype with Visily?
With Visily, you can create prototypes that let you see how your app screens will change and how your buttons will work. You can also add interactions and animations to make your prototype more realistic.
Here are the steps to create a prototype with Visily:
- First, you need to design your app screens using Visily’s powerful editor and AI features. Alternatively, You can choose from many templates or start from scratch.
- Next, you need to connect your screens to create a flow. You can do this by dragging and dropping lines between your components and the screens they lead to. For example, you can connect a button to the next screen that will appear when you click it.
- Finally, you need to present and share your prototype with others. You can choose to share your prototype as a slide presentation. You can also collect comments from your team and export your prototype to PDF.
For teams looking to streamline the prototyping process, leveraging AI-driven tools can be a game-changer. With Visily’s AI Prototype Generator, designers and non-designers alike can quickly generate high-fidelity prototypes, reducing time spent on manual design work and accelerating product development
Final Thoughts
Prototyping is a super important step when making digital products like apps and websites. You start with simple versions called low-fidelity prototypes. They help you see if your idea makes sense and if people can use it easily.
As you get more feedback from the stakeholders, you make better versions, called mid-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes. These are more detailed and start to look and work more like the final product. They help you make sure everything looks good and works well.
Using tools like Visily makes prototyping fun and easier. You can drag and drop to design your screens, connect them to show how they work together, and even add cool interactive parts. Then, you can show your prototype to others, get their thoughts, and keep making it better.
Remember, prototyping helps you test your ideas quickly, saves time and money, and helps you make a product that people will love to use. It’s a smart way to work together with your team and make sure you’re on the right track to creating a great final product.
The ultimate guide to digital Prototyping: top FAQs answered
What do you mean by prototyping?
Prototyping is the process of creating a preliminary version of a product, such as a website or app, to test and refine its design and functionality before developing the final version. It allows designers and stakeholders to explore ideas, gather feedback, and make improvements early in the development process.
What are the 3 types of prototyping?
The three main types of prototyping are:
- Low-fidelity prototyping: Simple, quick, and inexpensive prototypes using paper sketches or basic digital wireframes.
- Mid-fidelity prototyping: More detailed and interactive prototypes that simulate some functionality and navigation.
- High-fidelity prototyping: Realistic and fully functional prototypes that closely resemble the final product.
What are the 5 stages of prototyping?
The five stages of prototyping are:
- Conceptualization: Defining the purpose, goals, and requirements of the prototype.
- Design: Creating the visual and functional elements of the prototype.
- Development: Building the prototype using the appropriate tools and techniques.
- Testing: Evaluating the prototype with users and gathering feedback.
- Refinement: Iterating and improving the prototype based on the feedback received.
- What does prototyping mean in design?
In design, prototyping refers to the creation of a preliminary model or sample of a product to test its design, functionality, and user experience. It allows designers to experiment with different ideas, gather feedback from stakeholders, and make iterative improvements before investing in the final development.
What does prototype mean?
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is used to evaluate the feasibility, design, and functionality of a product before investing in full-scale production. Prototypes help in identifying potential issues, gathering user feedback, and refining the product to meet the desired goals.