When you have a cool idea for a new app or digital product, before you go all-in and build the whole thing, you want to make sure your idea is solid. Well, there are two ways you can bring your ideas to life before making the real thing: a Proof of Concept (POC) and a Prototype.
A Proof of Concept is a demonstration to verify that certain concepts or theories have the potential for real-world application. A PoC is typically used to assess the feasibility of the idea before substantial resources are committed to its development.
On the other hand, a prototype is a preliminary version of a digital product that visualizes how a product would look or function in the real world.
Both of these steps are super important in making your idea a success, and they help you understand what your users might need or want.
So let’s dive in and learn the difference between a Proof of Concept (PoC) and a Prototype!
POC vs Prototype: Key Differences
| Aspect | Proof of Concept (PoC) | Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Determine idea feasibility and technical aspects | Test usability, functionality, and design |
| Target Audience | Internal team, technical stakeholders | Stakeholders, investors, focus groups |
| Focus | Technical viability | User experience, design, functionality |
| Expectations | Technical validation | Draft of final product, visual representation |
| Usefulness for… | Deciding idea’s feasibility, technology choice | Visualizing flow, securing funding, feedback |
| Demonstrates | Feasibility of concept | UI/UX, specific functionality |
| Suitable for… | Sharing technical knowledge, technology choice | Securing funding, showcasing design and flow |
| Ideal Scenarios | When creating a revolutionary product | Tight deadlines, seed-stage funding, feedback |
Explore how Visily’s AI-powered prototyping tools can help bring your concepts to life efficiently
What’s a Proof of Concept (PoC)?
A proof of concept (PoC) is a feasibility study that validates the core functionality and feasibility of a product idea. It demonstrates the key business concepts with minimal features to gather initial user feedback. PoC projects require fewer resources than full product development to test assumptions quickly.

Creating a mobile app proof of concept (mobile app PoC) helps identify whether users respond positively before investing significant time and money into development. It focuses on the minimum viable product that attracts early adopters to provide feedback. An effective PoC shows the value proposition works technically to solve users’ pain points.
The iterative process continues by refining the working app with user input. Further prototypes add enhanced capabilities towards the final product vision. A mobile app PoC allows companies to verify product-market fit on a small scale first. It enables pivoting the concept quickly if needed, to align with user and market demand before full development.
Why Should You Initiate a PoC Project?
You should initiate a PoC project if you want to test the feasibility and potential of your idea before investing too much time and resources into it. A PoC project can help you:
- Validate your idea and show its value to your target audience, stakeholders, and investors.
- Mitigate risks and identify challenges and opportunities in the early stages of development.
- Plan better and improve your project definition, goals, and requirements.
- Save time and money by avoiding unnecessary, poorly planned, or unwanted projects that fail to meet customer needs.
- Gain trust and confidence from your team, clients, and partners by demonstrating your project viability and potential.
PoC Best Practices
To make sure your PoC rocks and you get the most out of it, here are some smart moves to follow:
Set Clear Goals:
Just like when you’re planning a science project, you need to know what you’re trying to prove. Decide what parts of your app idea you want to test, and make sure you’re not trying to do too much at once. Keep it simple and focused.
Figure Out What to Measure:
Imagine you’re experimenting. You need to know how to tell if it worked. Set up some clear signs or benchmarks that will show your PoC is successful.
Run Your PoC Project:
Now, get to work! Remember, a PoC is usually just looking at one special part of your app, not the whole thing. If you have a bunch of different things to test, you might need to run a few different PoCs.
Keep Track of Your Results:
As you test your idea, check to see if you’re hitting those benchmarks you set. This will tell you if your app idea is on the right track.
After you’ve done your PoC, you’ll know a lot more about what works and what doesn’t. If your idea looks good, you can take the next step and start making a more complete version, like a prototype or a minimum viable product (MVP). But if your PoC shows that your idea needs some changes, that’s okay too! It’s way better to figure this out now before you spend a lot of time and money.
What is Prototyping?
Prototyping is the process of creating a simplified version of a product concept that can be tested with target users and stakeholders.
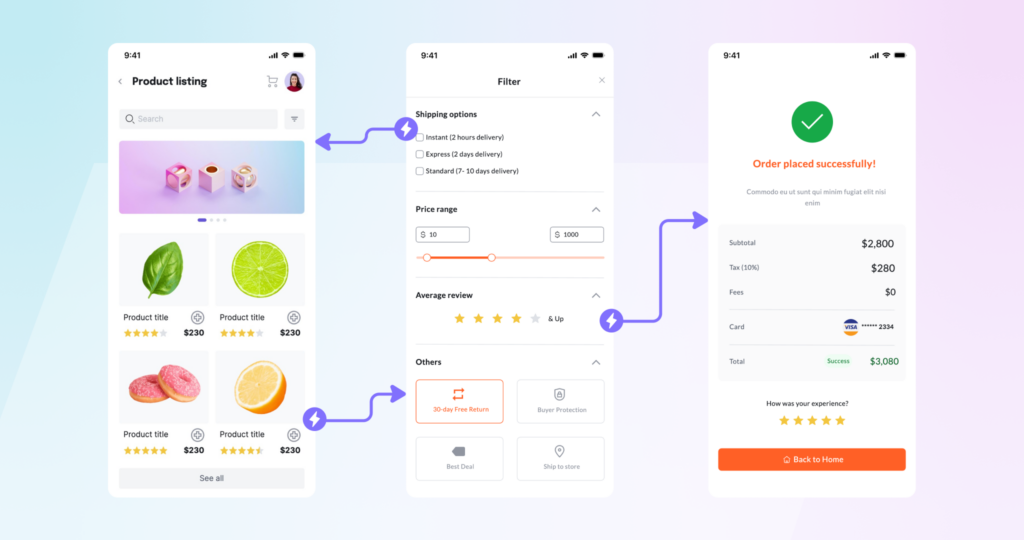
Prototyping is a common practice in software development, web development, and mobile app development. It helps to validate the idea, design, and functionality of the product before investing significant resources into development.
Why Should You Build a Prototype?
Creating a prototype is an invaluable part of any product development process. It allows you to test out concepts, get early feedback, and work out issues before investing heavily in coding and development. For startups and established companies alike, prototyping offers significant benefits. These benefits can minimize costs and risks. Simultaneously, these benefits can maximize the potential value derived from new product ideas.
Before you commit significant capital and resources to the production of an innovation, prototyping allows you to conduct market validation inexpensively. You can gather feedback from stakeholders to assess the product concept’s level of interest and fit. This feedback helps minimize the risk of developing and launching a digital product that fails to deliver value or address real market needs.
Prototyping helps reduce technical risks. It also prevents wasted efforts on ideas that are not technically feasible. Prototyping enables you to refine and iterate on the design before finalizing the product. Issues identified early on through prototyping will save significant time and costs. They save these resources compared to making changes further down the production cycle.
Prototyping delivers multidimensional value by taking a few key actions. First, it validates concepts through real-world testing. Second, it de-risks development processes. Third, it secures buy-in from stakeholders. Finally, it brings ideas to market faster and more successfully. The proof of concept and insights provided make prototyping an indispensable step. You need to take this step before committing to full production.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a Proof of Concept (PoC) and a prototype is key to creating a successful digital product. A PoC helps you figure out if your app idea is possible and if it can really help solve problems for users. It’s like a test run for your business concept that doesn’t use too many resources. With a PoC, you can make sure your idea makes sense before you dive in deeper.
On the other hand, a prototype is like a draft version of your app that visualizes how the app looks and works for people who might use it. It’s a great way to show your idea to others and get their thoughts on it.
Both PoCs and prototypes are super important steps in making your app idea come to life. They help you make sure your app will be something people really want. So, before you start building your app, remember to test your idea with a PoC and then make it real with a prototype. Start your prototyping journey today with Visily’s free and user-friendly prototyping too