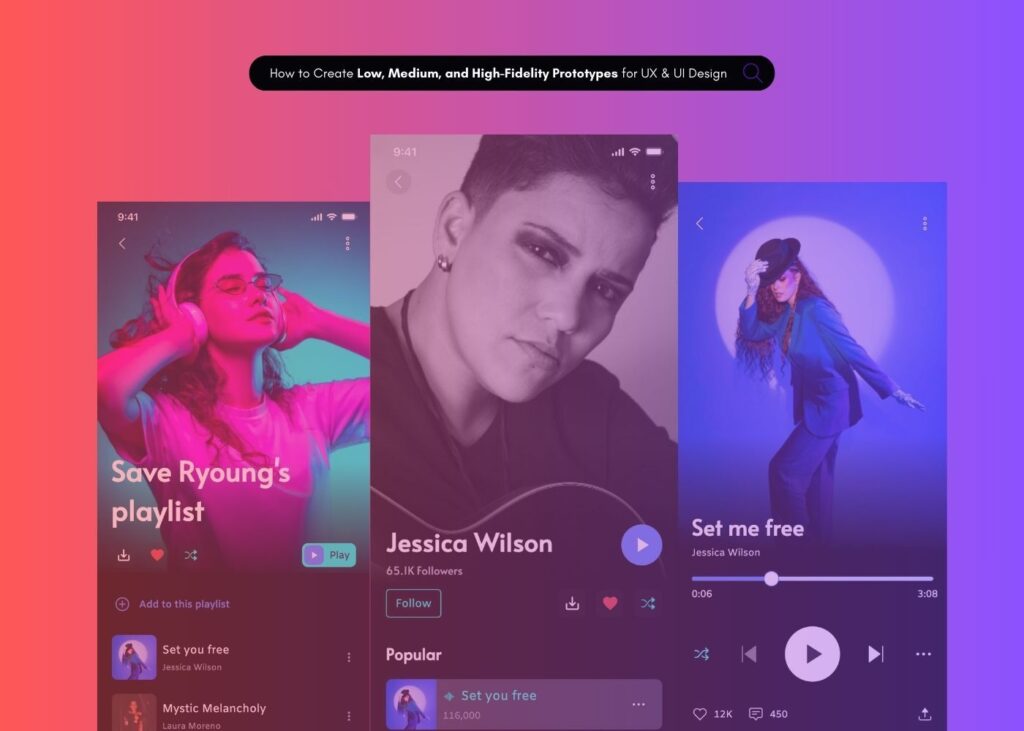
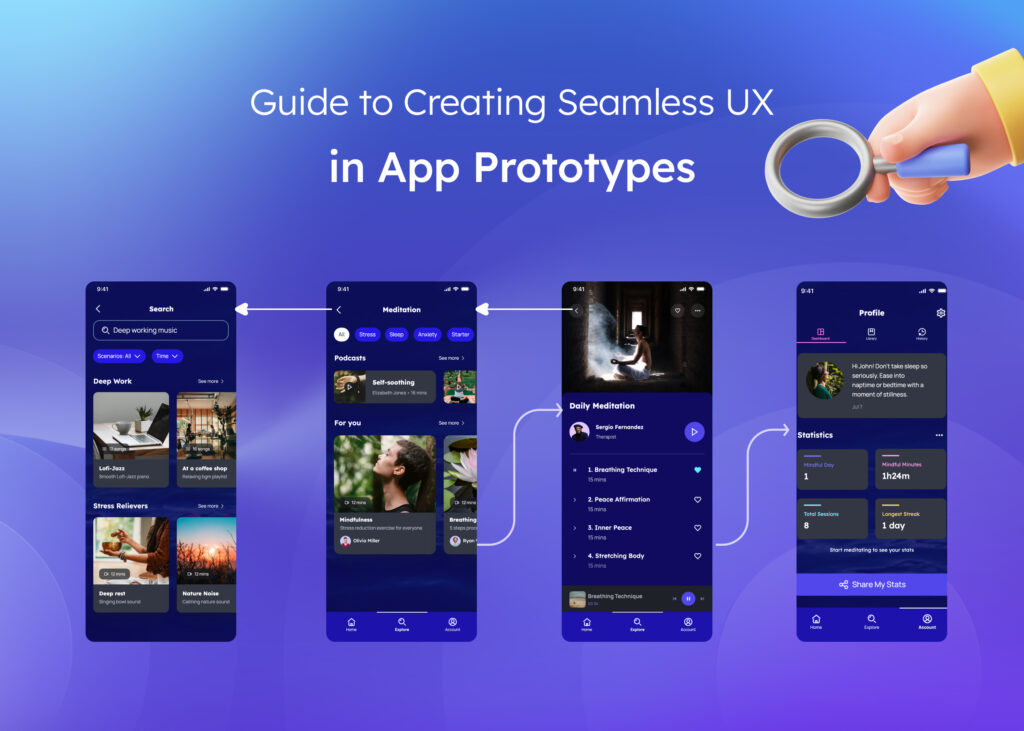
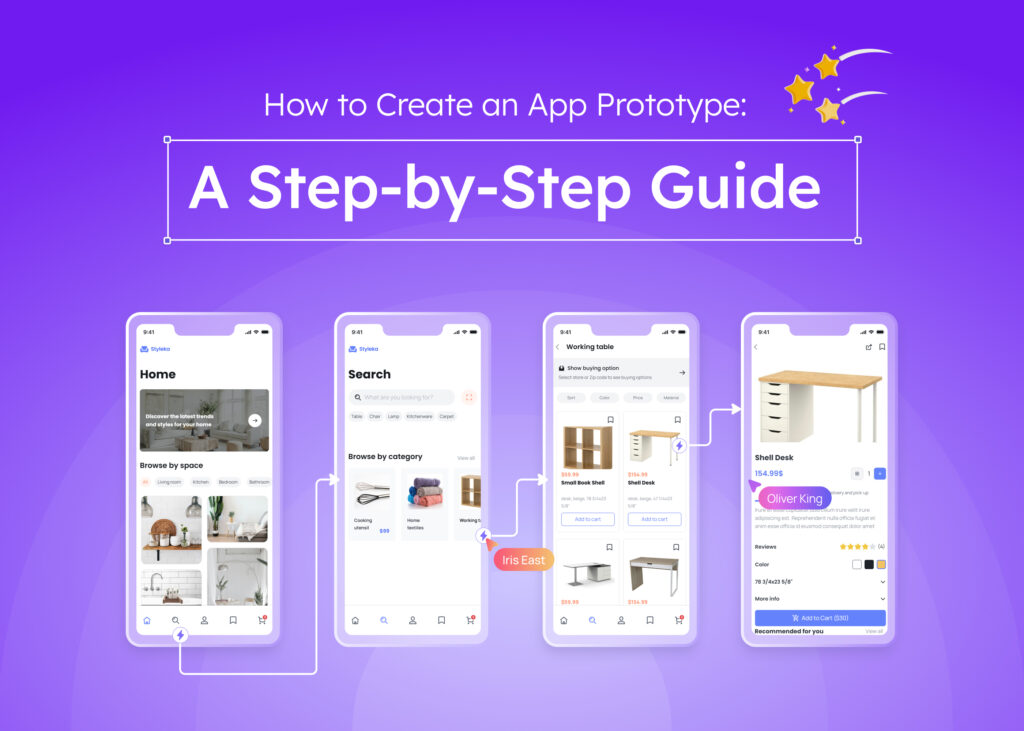
When starting an app development project, one of the most crucial decisions involves selecting the appropriate prototype fidelity level. The choice between low-fidelity vs high-fidelity prototype approaches significantly impacts your project timeline, budget, and ultimate success.
Why Does Fidelity Matter in Prototyping?
Fidelity in prototyping refers to how closely a prototype resembles the final product in terms of visual design, content, and interactivity. Making informed decisions about low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes has major implications for your development process and budget.
According to recent industry data, app design costs typically range from $3,000 to $15,000, with prototype development representing a significant portion of this investment. Your choice of prototype fidelity directly affects both your initial costs and potential revisions required later.
What Is a Low-Fidelity Prototype?
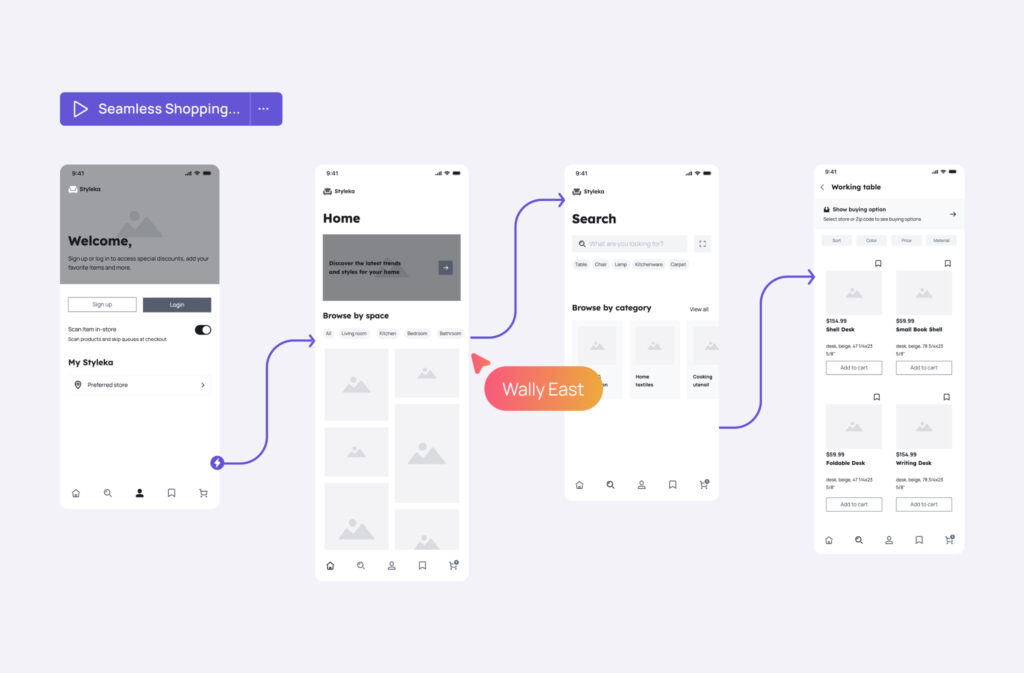
The question “What is a low-fidelity prototype?” often comes up during planning discussions. Simply put, low-fidelity prototypes are simplified representations focusing on core functionality rather than visual details. Paper sketches, basic wireframes, and simple digital mockups fall into this category.
Creating low-fidelity wireframes has become accessible even for non-designers using tools like Visily, which can quickly transform sketches or text descriptions into workable prototypes.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The advantages of low-fidelity prototype development make them particularly valuable when:
- Cost considerations matter: Low-fidelity prototypes typically range from $3,000 to $8,000, making them budget-friendly for early testing.
- Speed is essential: Teams can produce these prototypes in days rather than weeks, allowing for rapid iteration cycles.
- Focus needs to remain on functionality: Without visual distractions, stakeholders evaluate fundamental user flows more effectively.
- Flexibility for changes remains crucial: Modifications can be implemented quickly without significant resource investment.
- Team collaboration proves important: The simplicity encourages participation from various team members, not just designers.
However, the disadvantages of low-fidelity prototype approaches include the following:
- Minimal visual representation often fails to convey the final user experience adequately.
- Basic interactions may force users to imagine functionality rather than experience it directly.
- Stakeholders might struggle to visualize the final product from simplified representations.
- Complex interaction patterns don’t translate well in low-fidelity formats.
What Is a High-Fidelity Prototype?
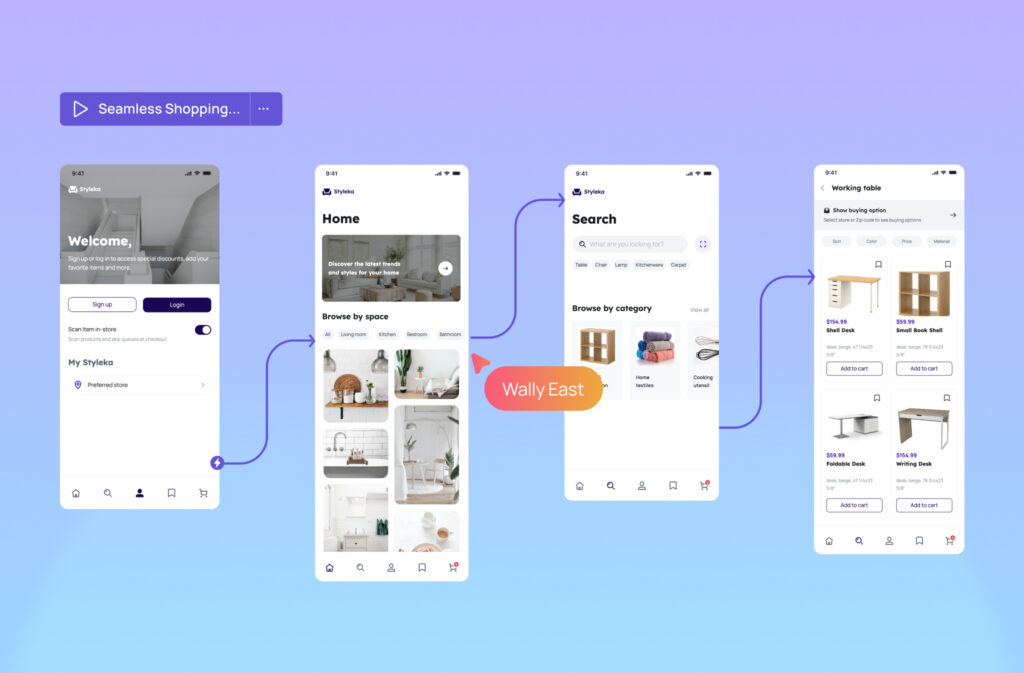
Moving up the spectrum, a high-fidelity prototype represents a detailed version closely resembling your final product in visual design, content, and interactivity. High-fidelity prototypes provide realistic previews of the user experience, making them invaluable for usability testing and stakeholder presentations.
Modern tools like Visily help transform low-fidelity wireframes into high-fidelity, interactive prototypes quickly, bridging the gap between concept and execution.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The advantages of high-fidelity prototype development include:
- User testing becomes significantly more accurate as interactions mirror the final product experience.
- Non-technical stakeholders understand the product vision more easily through detailed visualizations.
- Development risks decrease as teams identify usability issues before beginning expensive coding phases.
- Marketing efforts can begin earlier using the prototype for demonstrations and investor pitches.
- Complex interactions and animations receive proper testing and refinement before development.
On the flip side, the disadvantages of high-fidelity prototype approaches create several challenges:
- Costs rise substantially, with high-fidelity prototypes typically ranging from $15,000 to $30,000.
- Creation timelines extend to weeks rather than days, potentially slowing overall project momentum.
- Teams often resist substantial changes due to the increased time and resource investment.
- Reviewers might focus excessively on visual elements rather than core functionality.
- Testing sessions can derail completely when technical issues arise in complex prototypes.
Key Differences between Low vs. High-Fidelity Prototypes
Understanding the difference between high-fidelity and low-fidelity prototype approaches helps teams make informed decisions. Here’s a feature-by-feature comparison:
| Feature | Low Fidelity | High Fidelity |
| Development time | Days (1-2 weeks) | Weeks (2-12 weeks) |
| Cost range | $3,000-$8,000 | $15,000-$30,000+ |
| Visual detail | Minimal, wireframe-style | Detailed, final-product appearance |
| Interactivity | Limited or simulated | Functional buttons, transitions |
| User testing value | Concept validation | Usability and experience testing |
| Feedback focus | Core functionality | Visual design and interactions |
| Development stage | Early ideation | Later refinement |
| Revision ease | Simple and quick | Complex and time-consuming |
The low-fidelity prototype vs. high-fidelity decision ultimately depends on your project’s current phase and specific requirements.
Choosing the Right Fidelity for Your Needs
When deciding between low to high-fidelity prototypes, consider these factors:
- Project phase assessment shows early concept exploration benefits from low-fidelity, while pre-development refinement needs higher fidelity.
- Budget constraints with app design costs ranging widely from $3,000 to $50,000+ may dictate your approach by necessity.
- Timeline pressures can influence your choice, as low-fidelity prototypes take days while high-fidelity versions require weeks.
- Feedback goals vary widely—structural feedback works well with low-fidelity while detailed usability testing demands high-fidelity approaches.
- Audience needs differ greatly, as technical teams understand low-fidelity prototypes while executives or clients might require high-fidelity versions.
Many successful projects use a progressive approach, starting with low-fidelity prototypes and gradually transitioning to higher fidelity as concepts prove viable. Visily’s prototyping tools support this evolution seamlessly, making it easy to transform initial concepts into interactive prototypes.
Conclusion
The debate between low-fidelity vs high-fidelity prototype approaches isn’t about finding a single “best” option but selecting what serves your current needs most effectively. Both play valuable roles in the design process.
Low-fidelity prototypes excel at cost-effective exploration and rapid iteration. High-fidelity prototypes deliver greater value for detailed refinement and stakeholder communication. Many projects benefit from starting with low-fidelity prototyping and progressively increasing fidelity as concepts solidify.
Modern tools like Visily bridge this gap by allowing teams to efficiently transform rough concepts into detailed prototypes, optimizing both cost and time investments throughout the design process.
Low vs. High Fidelity Prototypes Explained: Your FAQ Guide
How much does a low-fidelity prototype typically cost?
Low-fidelity prototypes generally cost between $3,000 and $8,000, depending on complexity and the number of screens required.
What’s the average development time for a high-fidelity prototype?
High-fidelity prototypes typically take 2-12 weeks to develop, with more complex apps requiring longer timeframes.
Can projects skip low-fidelity prototyping and go straight to high-fidelity?
While possible, skipping low-fidelity prototyping often leads to more expensive revisions later, as fundamental issues aren’t identified early.
Which tools work best for creating prototypes of different fidelities?
Visily excels at both low and high-fidelity prototyping, allowing teams to start simple and progressively enhance their designs.
When should teams transition from low to high-fidelity prototyping?
Transition when core concepts receive validation, user flows make sense, and more detailed feedback on interactions and visual design becomes necessary.